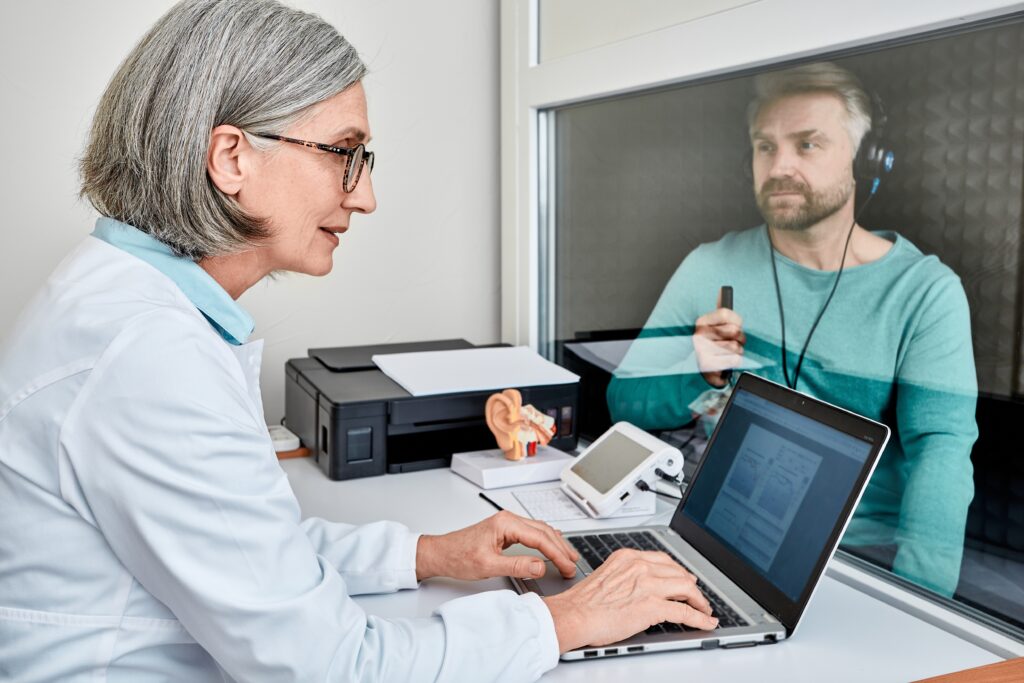
Hearing Test
Hearing Test
A hearing test, also known as a hearing exam or audiogram, is performed to determine if hearing loss is present, and if so, the severity of the hearing loss, how well the ear drum and middle ear is functioning and your ability to understand speech in quiet and background noise. Individuals often self-refer for hearing evaluations because they notice they are not hearing well and would like to confirm their hearing levels. Others are referred for a hearing evaluation by their physician for the following reasons:

Insurance Coverage
Peninsula Hearing Services is in-network with most major PPO health insurance plans for a hearing test, including Medicare, Cigna, Anthem Blue Cross, Blue Shield, United Healthcare, Aetna, TriCare, Medi-Cal, Care Advantage and the HMO plan Hills Physician’s Medical Group. The office is not in-network with HMO’s from Kaiser, Sutter, or the Palo Alto Medical Foundation.
In general, insurance plans will cover most or all of the cost of a hearing test. However, each individual plan can vary regarding deductibles, copays and annual out-of-pocket minimums that might be required to be met before a health insurance will pay for some or all medical visits and/or treatments.
Contact you insurance company using the customer service phone number on the back of your insurance card if you have any questions about your insurance coverage before your visit.
What Tests Will Be Done?
A Doctor of Audiology will perform the hearing test. This includes video otoscopy, pure-tone testing, bone-conduction testing, speech testing in quiet and in-noise, tympanometry and otoacoustic emissions testing. For patients who experience tinnitus, a tinnitus evaluation will be performed. The hearing test is approximately 30-40 minutes in length and the results are immediate.
Each subtest is painless and some take as little as 1 minute to complete. It is common for many patients to arrive anxious not knowing what to expect. The hearing exam results and audiogram will be reviewed with you at the visit. If a medical condition is found, you will be referred to a specialist. If a recommendation is made for hearing aids, they may be ordered through Peninsula Hearing Services. The audiologist will advise the best hearing aid 2023 for you and provide details with how they can be ordered.
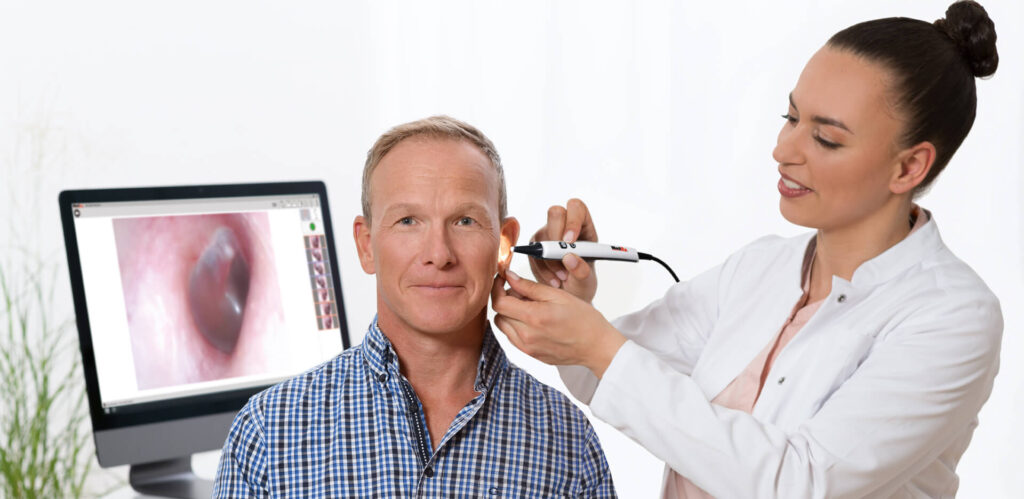
Otoscopy
Otoscopy is a magnifying instrument that shines a beam of with a light in your ear canal for a healthcare provider to visualize the health of the ear canal and ear drum. This allows the examiner to assess the general health of the ear canal, including whether excessive cerumen (ear wax) is present or if a perforation (hole) in the ear drum is present. Peninsula Hearing Services utilizes video otoscopy so that the patient can see their ear canal and ear drum on a monitor.
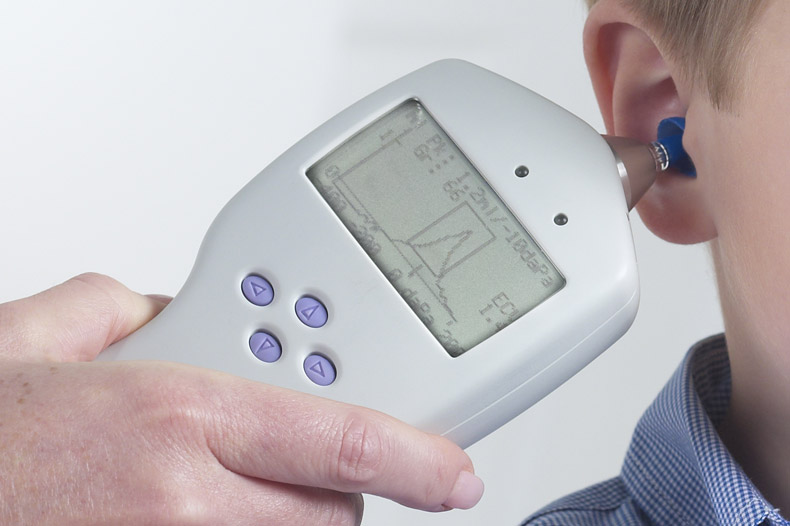
Tympanometry
A tympanometer is a handheld instrument that blows a gentle puff-of-air and presents several tones into the ear canal to evaluate how well the ear drum vibrates to sound, the pressure behind the ear drum and whether a perforation or hole in the ear drum exists. The resulting information from the test is referred to as tympanometry. This test is important to determine the overall health and functioning of the ear drum and middle ear cavity.
Pure-Tone Air and Bone Conduction Testing
Using headphones in a sound-treated hearing booth, a pure tone hearing test uses air conduction testing to determine the quietest tones that a person can hear at different pitches or tones. The test measures sound as it travels from the opening of the ear, down the ear canal, through the ear drum and middle ear space to the hearing nerve. It is somewhat similar to an eye exam in which an optometrist evaluates the smallest letters that each eye can see clearly.
Bone-conduction testing measures the same tones as pure tone air conduction. A specialized headset named a bone-vibrator is placed behind one ear and sound is transmitted, through vibration of the skull directly to the hearing nerve.
These two different measurements determine if hearing loss originates from the ear canal and ear drum space or from the hearing nerve deep inside the brain.
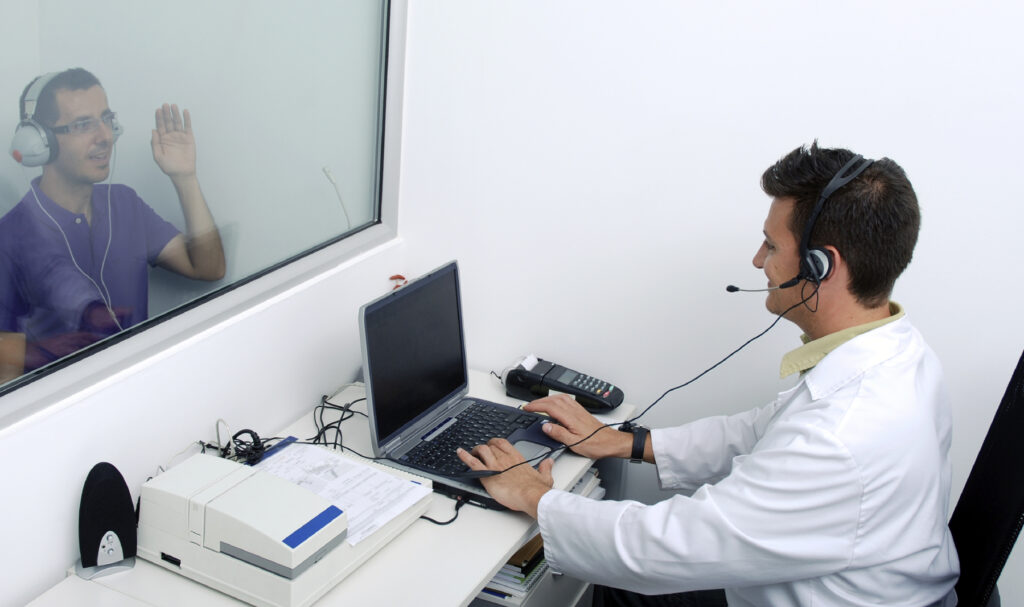
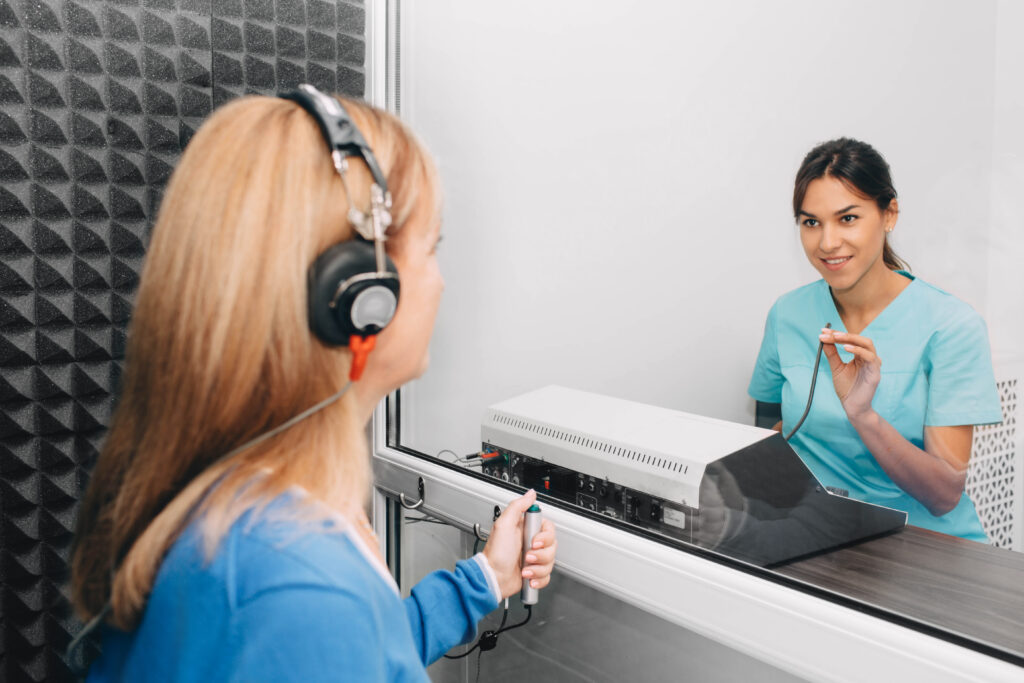


Speech Testing
Under headphones, speech testing measures how well you understand speech at your optimum hearing level. The examiner presents a standardized list of words that you will be asked to repeat back. This test is important to assess the health of the hearing nerve and, if hearing loss is present, guide treatment options, as some people report they can hear sound, but the speech is distorted, no matter how loud the volume level.
Speech-in-Noise (SIN) Testing
Speech-in-noise testing assesses how well one hears in various levels of background noise. Using a CD, 6 short sentences with increasing levels of noise are presented The patient is tasked with repeating each sentence back as best they can. At the end of the 6th sentence, a score is tabulated that identifies degree of difficulty understanding speech in noise.
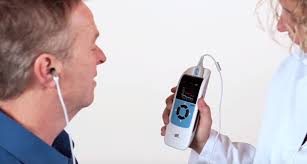
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) Testing
Otoacoustic emissions testing measures how well specific inner ear nerve receptors named “outer hair cells” are functioning. Using a handheld instrument, a soft ear tip similar to an earbud is placed in the ear and gentle melody of tones is presented to the ear. The nerve receptors of a healthy hearing nerve will emit robust responses that are received and assessed by the instrument as “normal”, “borderline” or “absent”. This test is highly sensitive to changes in hearing that often are not detected by simple pure-tone and bone conduction testing.
Tinnitus Assessment Testing
A tinnitus assessment allows the healthcare provider to identify a) the specific tone or pitch of the reported tinnitus b) the volume or intensity of the tinnitus c) whether “white noise” or static can make the tinnitus go away (a term known as masking). The results of this test are useful for diagnosis of the problem that might be causing the tinnitus as well as prognosis for certain treatments, if needed.